Introduction
Last time, from the functions of "VMware SD-WAN", I explained the characteristic functions that cannot be realized with SD-WAN products of other companies. In this article, I will introduce what kind of configuration should be used and what points should be noted when deploying VMware SD-WAN.
Conventional WAN Issues
First, when considering the introduction of VMware SD-WAN, I would like to consider a general corporate WAN configuration as an example.
Many companies in Japan use a high-quality, bandwidth-guaranteed closed network as the main line between their headquarters or data center and bases all over the country, and a cheap, best-effort broadband line as a backup line. The configuration used was the mainstream. In addition, the business application server was also located within the company, and access to the Internet was via the head office or data center only. (Fig. 1).
Figure 1: Conventional WAN configuration and communication path
However, due to the increase in the use of the cloud for business applications and the use of large-capacity content, the amount of communication between the head office and bases has increased dramatically, and more and more companies are suffering from pressure on line capacity and increased load on proxy servers. I was. In addition, since many applications now use SSL communication, it is no longer possible to simply control communication with a firewall, and the need for communication control for each application has arisen.
To solve these problems, VMware SD-WAN realizes application visualization and controls communication paths by replacing the routers at each location (Fig. 2). Although it is assumed that you will replace the Router, you can select the installation method from several patterns based on the existing network configuration.
Figure 2: Communication path after installing VeloCloud
Deployment patterns at bases
In the deployment at bases, VMware SD-WAN Edge is the default gateway for all traffic within the bases, with an "In-Path" configuration and an L3 switch in the LAN. You can select the "Off-Path" configuration that becomes the default gateway and installs VMware SD-WAN Edge above it.
In-Path Configuration
The LAN in the base is configured only with L3 switches and L2 switches, and VMware SD-WAN Edge serves as the default gateway for all traffic and operates in a DHCP environment. If so, it is easy to migrate (Figure 3). However, if VMware SD-WAN Edge becomes a failure, traffic will be affected, so it is recommended to deploy in an HA configuration.
Figure 3: Edge installation configuration (In-Path) at bases
Off-Path Configuration
The default gateway for all traffic is an L3 switch, and VMware SD-WAN Edge is installed above it, so VMware SD-WAN Edge fails. can automatically switch to the other line (Fig. 4).
Figure 4: Edge deployment configuration of data center (Off-Path)
Deployment patterns in data centers
In deployments in data centers, VMware SD-WAN Edge can be used in "Two-Arm" mode or "One-Arm" mode while keeping routers and firewalls that serve as Internet gateways. Arm" mode can be selected (Fig. 5).
Figure 5: Data center Edge deployment configuration
Two-Arm mode is characterized by a simple network configuration and easy control because the overlay and underlay interfaces are clearly separated. One-Arm mode, on the other hand, uses a single physical interface for overlay and underlay communication, minimizing the impact on existing networks.
Either mode can flexibly support the configuration of the existing network, so please select according to the configuration and degree of impact.
In addition, if the data center is a Backhaul Hub and communication from each base is routed through the data center, it is necessary to be able to access VMware SD-WAN Edge, which is the hub, from each base using UDP 2426 over the Internet. Therefore, please set port forward to VMware SD-WAN Edge at the data center internet gateway.
Firewall and VMware SD-WAN Edge configuration
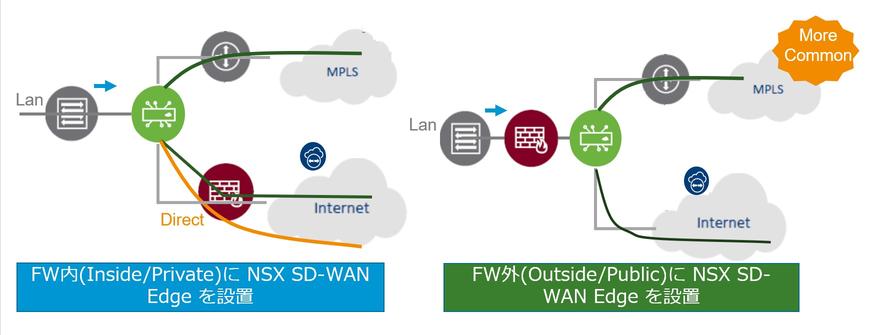
If you have a firewall installed at each location to control communication and visualize applications, use VMware SD-WAN Edge and firewall Note that the network design will change depending on the network configuration of the wall.
In general, VMware SD-WAN Edge should be configured outside the firewall so that communication control by the firewall does not affect visualization. If the configuration is reversed, the traffic transferred to the overlay will be encrypted, and the firewall will not be able to control the communication (Figure 6).
Figure 6: FW and Edge configuration
Creating an overlay network with Cloud VPN
Conventional base-to-base VPN requires VPN connection settings for each device, but VMware SD-WAN Edge enables one-click VPN connection using the Cloud VPN function. achieve the expansion of In addition to eliminating the need for troublesome N x N manual tunnel settings, IPsec interconnection with legacy routers at sites where VeloCloud is not installed is also possible.
In the case of a site that uses both a closed network and the Internet network, it is possible to communicate between sites using a closed network only by routing control without building an overlay network with Cloud VPN, but priority control of business policy Do not forget to set up an overlay network when using bandwidth control, as it is essential to set it up (Fig. 7).
Figure 7: CloudVPN and overlay
Underlay and Overlay Routing
Routing by VMware SD-WAN Edge consists of an underlay network, which is a conventional physical network, and a virtual overlay network between VMware SD-WAN Edges. I have. Route information is exchanged between these networks by VeloCloud Controller, but if the route information of a certain base is learned from both networks, it will be impossible to determine which route information should be referred to for communication. As a precaution when performing routing, it is fundamental to design routing so that route information learned from the overlay is not redistributed to the underlay.
In addition, these controls are realized by overlay flow control (OFC) function separately from routing control such as static, OSPF, BGP.
Overlay flow control holds all the route information learned by each VMware SD-WAN Edge and the connection points for it as an OFC table. We are prioritizing the connection points to the underlay.
Routing is based on appropriate filtering and route information management by OFC, so we recommend designing according to best practices.
Hardware, License, and Edition Selection
Finally, I will explain hardware, license, and edition selection.
Hardware and license selection
First, the maximum throughput, number of VPN tunnels, and number of ports differ for each hardware, so select according to your requirements. Next, select the license for the bandwidth used in the overlay. Since the license allows the maximum throughput of the overlay in stages, please select a bandwidth with a margin. For example, if you need 350Mbps bandwidth in your overlay, choose Edge610 or higher (Table 1).
Table 1: Supported bandwidth for each device
Selecting an Edition
There are three types of editions according to their usage. Choose an edition that supports the features you need. It is divided into "Standard", which is for limited environments at a reduced price, "Enterprise", which provides standard functions in general environments, and "Premium", which supports SaaS services using cloud gateways and connections with legacy routers ( Table 2), Enterprise should be selected if you do not use SaaS services by cloud gateways.
Table 2: List of features for each edition
Conclusion
In this article, I introduced what kind of configuration should be used and what points should be noted when introducing VMware SD-WAN.
Next time, I will introduce the benefits obtained by deploying VMware SD-WAN. In particular, we will explain in detail how much cost can be reduced by automatically identifying line quality.

![EVsmart blog Toyota's electric car "bZ4X" that makes you feel comfortable with electric cars and quick chargers / No% display of battery level [Editorial department] Popular articles Recent posts Category](https://website-google-hk.oss-cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com/drawing/article_results_9/2022/3/9/752542064665dc2bd7addbc87a655694_0.jpeg)
![Lenovo's 8.8 inch one-handed tab "Legion Y700" full specs released! [Is the price in the 40,000 yen range?]](https://website-google-hk.oss-cn-hongkong.aliyuncs.com/drawing/article_results_9/2022/3/9/207e1be231154e91f34c85b4b1d2126c_0.jpeg)